二叉树(Binary Tree)
4.8.1、二叉树定义
二叉树(Binary tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型。许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构往往是二叉树形式,即使是一般的树也能简单地转换为二叉树,而且二叉树的存储结构及其算法都较为简单,因此二叉树显得特别重要。二叉树特点是每个结点最多只能有两棵子树,且有左右之分。
二叉树是n个有限元素的集合,该集合或者为空、或者由一个称为根(root)的元素及两个不相交的、被分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成,是有序树。当集合为空时,称该二叉树为空二叉树。在二叉树中,一个元素也称作一个结点
满二叉树:如果一棵二叉树只有度为0的结点和度为2的结点,并且度为0的结点在同一层上,则这棵二叉树为满二叉树
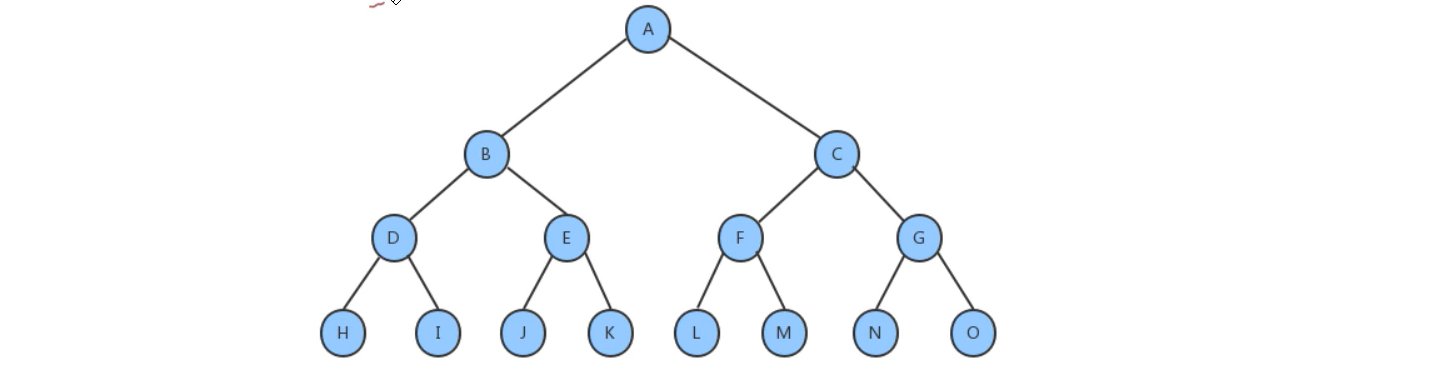
完全二叉树:深度为k,有n个结点的二叉树当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为k,有n个结点的满二叉树中编号从1到n的结点一一对应时,称为完全二叉树。完全二叉树的特点是叶子结点只可能出现在层序最大的两层上,并且某个结点的左分支下子孙的最大层序与右分支下子孙的最大层序相等或大1。
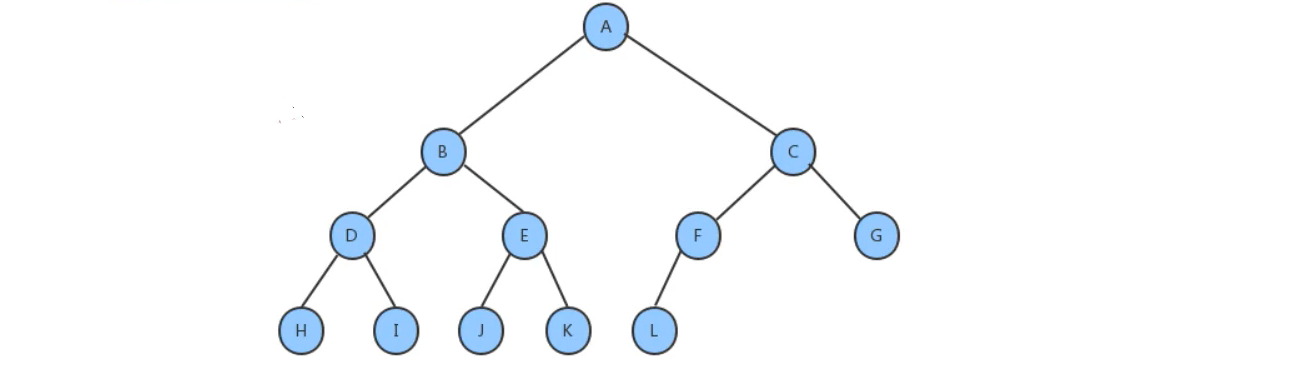
4.8.2、二叉查找树的创建
4.8.2.1、二叉树的节点类
二叉树其实就是由一个一个的结点及其之间的关系组成
结点类API设计
| 类名 | Node |
|---|---|
| 成员变量 | public Node left:记录左结点 public Node right:记录右几点 public Key key:存储键 public Value value:存储值 |
| 构造方法 | Node(Key key,Value value,Node left,Node right):创建Node对象 |
代码实现
private class Node<Key key,Value value>{
//存储键
public Key key;
//存储值
public Value value;
//记录左子节点
public Node left;
//记录右子节点
public Node right;
public Node(Key key,Value value,Node left,Node right){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
4.8.2.2、二叉查找树API设计
| 类名 | BinaryTree |
|---|---|
| 构造方法 | BinaryTree():创建BinaryTree对象 |
| 成员变量 | pricate Node root:记录根节点 private int N:记录树中元素个数 |
| 成员方法 | public void put(Key key,Value value):向树种插入一个键值对 private Node put(Node x,Key key,Value value):给指定树x上添加一个键值对,并返回添加后的新树 public Value get(Key ke):根据key查找树的值 private Value get(Node x,Key key):从指定的树x中找出key对应的值 public voide delete(Key key):根据key删除树对应位置的值 public Node delete(Node x,Key key):删除指定树x为key的键值对,并返回删除后的树 public int size():获取树的元素个数 |
4.8.2.3、二叉查找树实现
插入元素思想:
- 如果当前树中没有任何一个结点,则直接把新节点作为根结点使用
- 如果当前树不为空,则从根结点开始
- 如果新结点的key小于当前结点的key,则继续找当前结点的左子节点
- 如果新节点的key大于当前结点的key,则继续找当前结点的右子节点
- 如果新节点的key等于当前结点的key,替换该结点的value值即可
实现类
package cn.test.algorithm.datastruct;
public class BinaryTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private Node root;
private int N;
private class Node {
public Key key;
public Value value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
root = put(root, key, value);
}
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) {
//如果x子树为空
if (x == null) {
N++;
return new Node(key, value, null, null);
}
//如果x子树不为空
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
x.right = put(x.right, key, value);
} else if (cmp < 0) {
x.left = put(x.left, key, value);
} else {
x.value = value;
}
return x;
}
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
//如果x为null
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
//如果x子树不为空
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
return get(x.right, key);
} else if (cmp < 0) {
return get(x.left, key);
} else {
return x.value;
}
}
public void delete(Key key) {
delete(root, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
//x为null
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
//如果x子树不为空
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
x.right = delete(x.right, key);
} else if (cmp < 0) {
x.left = delete(x.left, key);
} else {
N--;
//删除x结点
//首先找到右子树中最小的节点
if (x.right == null) {
return x.left;
}
if (x.left == null) {
return x.right;
}
Node minNode = x.right;
while (minNode.left != null) {
minNode = minNode.left;
}
//删除右子树中最小的结点
Node n = x.right;
while (n.left != null) {
if (n.left.left == null) {
n.left = null;
} else {
n = n.left;
}
}
//让x的左子树称为minNode的左子树
minNode.left = x.left;
//让x的右子树作为minNode的右子树
minNode.right = x.right;
//让x结点称为minNode
x = minNode;
}
return x;
}
}
测试类
package cn.test.algorithm.test;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.BinaryTree;
public class BinaryTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<Integer, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.put(1, "张三");
tree.put(2, "王五");
tree.put(3, "赵六");
tree.put(4, "李七");
System.out.println("元素个数:" + tree.size());
System.out.println("键为3的元素值:" + tree.get(3));
tree.delete(2);
System.out.println("元素个数:" + tree.size());
System.out.println("键为3的元素值:" + tree.get(2));
}
}
运行结果
元素个数:4
键为3的元素值:赵六
元素个数:3
键为3的元素值:null
4.8.3、二叉查找树中最大和最小键
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public Key min() | 找出最小key |
| private Node min(Node x) | 找出指定树x中,最小键的结点 |
| public Key max() | 找出最大key |
| private Node max(Node x) | 找出指定树x中,最大键的结点 |
方法实现
private Node min(Node x) {
if (x.left != null) {
return min(x.left);
}
return x;
}
public Key max() {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return max(root).key;
}
public Node max(Node x) {
if (x.right != null) {
return max(x.right);
}
return x;
}
4.8.4、二叉查找树的基础遍历
二叉树遍历的三种方式:
- 前序遍历:先访问根结点,然后再访问左子树,最后访问右子树
- 中序遍历:先访问左子树,然后再访问根结点,最后访问右子树
- 后续遍历:先访问左子树,然后再访问右子树,最后访问根结点

4.8.4.1、前序遍历实现
设计方法:
- public Queue
preErgoic():使用前序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键 - private void preErgodic(Node x,Queue
keys):使用前序遍历,把指定树x的所有键存放的到keys队列中。
实现步骤:
- 把当前结点的key存放到队列中
- 找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树
- 找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树
实现方法
public Queue<Key> preErgodic() {
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
preErgodic(root, keys);
return keys;
}
private void preErgodic(Node x, Queue<Key> keys) {
if (x == null) {
return;
}
//把x的key放到队列中
keys.enqueue(x.key);
//查看是否有左子树
if (x.left != null) {
preErgodic(x.left, keys);
}
//递归比遍历右子树
if (x.right != null) {
preErgodic(x.right, keys);
}
}
测试类
package cn.test.algorithm.test;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.BinaryTree;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.Queue;
public class BinaryTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.put("E", "5");
tree.put("B", "2");
tree.put("G", "7");
tree.put("A", "1");
tree.put("D", "4");
tree.put("F", "6");
tree.put("H", "8");
tree.put("C", "3");
Queue<String> keys = tree.preErgodic();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = tree.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "====" + value);
}
}
}
测试结果
E====5
B====2
A====1
D====4
C====3
G====7
F====6
H====8
4.8.4.2、中序遍历实现
设计方法:
- public Queue
midErgoic():使用中序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键 - private void midErgodic(Node x,Queue
keys):使用中序遍历,把指定树x的所有键存放的到keys队列中。
实现步骤:
- 找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树
- 把当前结点的key存放到队列中
- 找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树
实现方法
public Queue<Key> midErgodic() {
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
midErgodic(root, keys);
return keys;
}
private void midErgodic(Node x, Queue<Key> keys) {
if (x == null) {
return;
}
//查看是否有左子树
if (x.left != null) {
midErgodic(x.left, keys);
}
//把x的key放到队列中
keys.enqueue(x.key);
//递归比遍历右子树
if (x.right != null) {
midErgodic(x.right, keys);
}
}
测试类
package cn.test.algorithm.test;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.BinaryTree;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.Queue;
public class BinaryTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.put("E", "5");
tree.put("B", "2");
tree.put("G", "7");
tree.put("A", "1");
tree.put("D", "4");
tree.put("F", "6");
tree.put("H", "8");
tree.put("C", "3");
Queue<String> keys = tree.midErgodic();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = tree.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "====" + value);
}
}
}
测试结果
A====1
B====2
C====3
D====4
E====5
F====6
G====7
H====8
4.8.4.3、后序遍历实现
设计方法:
- public Queue
afterErgoic():使用后序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键 - private void afterErgodic(Node x,Queue
keys):使用后序遍历,把指定树x的所有键存放的到keys队列中。
实现步骤:
- 找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树
- 找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树
- 把当前结点的key存放到队列中
实现方法
public Queue<Key> afterErgodic() {
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
afterErgodic(root, keys);
return keys;
}
private void afterErgodic(Node x, Queue<Key> keys) {
if (x == null) {
return;
}
//查看是否有左子树
if (x.left != null) {
afterErgodic(x.left, keys);
}
//递归比遍历右子树
if (x.right != null) {
afterErgodic(x.right, keys);
}
//把x的key放到队列中
keys.enqueue(x.key);
}
测试类
package cn.test.algorithm.test;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.BinaryTree;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.Queue;
public class BinaryTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.put("E", "5");
tree.put("B", "2");
tree.put("G", "7");
tree.put("A", "1");
tree.put("D", "4");
tree.put("F", "6");
tree.put("H", "8");
tree.put("C", "3");
Queue<String> keys = tree.afterErgodic();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = tree.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "====" + value);
}
}
}
测试结果
A====1
C====3
D====4
B====2
F====6
H====8
G====7
E====5
4.8.5、二叉查找树的层序遍历
所谓层序遍历就是从根结点第一层开始,依次向下,获取每一层所有结点的值。还是上面的树,遍历的结果为:EBGADFHC
设计方法:
- public Queue
layerErgoic():使用层序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键
实现步骤
- 创建队列,存储每一层的节点
- 使用循环从队列中弹出一个结点
- 获取当前结点的key
- 如果当前结点的左子结点不为空,则把左子结点放入到队列中
- 如果当前结点的右子结点不为空,则把右子结点放入到队列中
实现方法
public Queue<Key> layerErgodic() {
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
Queue<Node> nodes = new Queue<>();
//默认往队列中放入根结点
nodes.enqueue(root);
while (!nodes.isEmpty()) {
Node n = nodes.dequeue();
keys.enqueue(n.key);
if (n.left != null) {
nodes.enqueue(n.left);
}
if (n.right != null) {
nodes.enqueue(n.right);
}
}
return keys;
}
测试类
package cn.test.algorithm.test;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.BinaryTree;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.Queue;
public class BinaryTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.put("E", "5");
tree.put("B", "2");
tree.put("G", "7");
tree.put("A", "1");
tree.put("D", "4");
tree.put("F", "6");
tree.put("H", "8");
tree.put("C", "3");
Queue<String> keys = tree.layerErgodic();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = tree.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "====" + value);
}
}
}
测试结果
E====5
B====2
G====7
A====1
D====4
F====6
H====8
C====3
4.8.6、二叉查找树的最大深度问题
给定一棵树,请计算树的最大深度,还是以前面的树为例,这里最大深度为4
设计方法:
- public int maxDepth():计算整个树的最大深度
- private int maxDepth(Node x):计算指定树x的最大深度
实现步骤
- 如果根结点为空,则最大深度为0
- 计算左子树的最大深度
- 计算右子树的最大深度
- 当前树的最大深度=左子树的最大深度和右子树的最大深度的最大值+1
实现方法
public int maxDepth() {
return maxDepth(root);
}
public int maxDepth(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return 0;
}
int max = 0;
int maxLeft = 0;
int maxRight = 0;
if (x.left != null) {
maxLeft = maxDepth(x.left);
}
if (x.right != null) {
maxRight = maxDepth(x.right);
}
max = maxLeft > maxRight ? maxLeft + 1 : maxRight + 1;
return max;
}
测试类
package cn.test.algorithm.test;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.BinaryTree;
import cn.test.algorithm.datastruct.Queue;
public class BinaryTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.put("E", "5");
tree.put("B", "2");
tree.put("G", "7");
tree.put("A", "1");
tree.put("D", "4");
tree.put("F", "6");
tree.put("H", "8");
tree.put("C", "3");
System.out.println("最大深度:" + tree.maxDepth());
}
}
测试结果
最大深度:4
4.8.7、折纸问题
请把一段纸条竖着放在桌子上,然后从纸条的下边向上方对折1次,压出折痕后展开。此时折痕是凹下去的,即折痕突起的方向指向纸条的背面。如果从纸条的下边向上方连续对折2次,压出折痕后展开,此时有三条折痕,从上到下依次是下折痕、下折痕和上折痕。给定一个输入参数N,代表纸条都从下边向上方连续对折N次,请从上到下打印所有折痕的方向。
实现类
package cn.test.algorithm.datastruct;
public class PageFoldingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printTree(createTree(3));
}
//生成折痕树
public static Node<String> createTree(int N) {
//初始化一个根结点
Node<String> root = null;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
//产生第一次折痕
if (i == 0) {
root = new Node<>("down", null, null);
continue;
}
//队列进行遍历
Queue<Node<String>> queue = new Queue<>();
queue.enqueue(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//从队列弹出一个结点
Node n = queue.dequeue();
if (n.left != null) {
queue.enqueue(n.left);
}
if (n.right != null) {
queue.enqueue(n.right);
}
//如果都为空说明是叶子结点,所以需要在左右都插入两个结点
if (n.left == null && n.right == null) {
n.left = new Node("down", null, null);
n.right = new Node("up", null, null);
}
}
}
return root;
}
//打印树
public static void printTree(Node<String> root) {
//采用中序遍历
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left != null) {
printTree(root.left);
}
System.out.println(root.item + " ");
if (root.right != null) {
printTree(root.right);
}
}
//结点内部类
private static class Node<T> {
private Node left;
private Node right;
private T item;
public Node(T item, Node left, Node right) {
this.item = item;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
 Electron页面跳转、浏览器打开链接和打开新窗口
Electron页面跳转、浏览器打开链接和打开新窗口 前一篇博客中已经说过Golang对Gzip的处理,其实这是我的服务器端的处理,那么当我们服务器返回Gzip压缩的字符串后,客户端如何进行解压呢?本文主要记录下JavaScript对Gzip进行压缩和解压处理。
前一篇博客中已经说过Golang对Gzip的处理,其实这是我的服务器端的处理,那么当我们服务器返回Gzip压缩的字符串后,客户端如何进行解压呢?本文主要记录下JavaScript对Gzip进行压缩和解压处理。 我们在工作或是生活中,有时会需要制作一些请柬、奖状、或者桌牌等,这些东西都有一个共性,那就是除了每个人的名字不一样之外,其他大部分内容都是一样的,那么我们可以如何快速地批量制作呢?很简单,用Word的邮件合并功能就能做到!
我们在工作或是生活中,有时会需要制作一些请柬、奖状、或者桌牌等,这些东西都有一个共性,那就是除了每个人的名字不一样之外,其他大部分内容都是一样的,那么我们可以如何快速地批量制作呢?很简单,用Word的邮件合并功能就能做到! 桌面应用很多都会在系统托盘中出现,那么Flutter的开发的桌面应用该如何增加到系统托盘中呢?本文将带大家一起尝试一下.
桌面应用很多都会在系统托盘中出现,那么Flutter的开发的桌面应用该如何增加到系统托盘中呢?本文将带大家一起尝试一下. Python调用WPS把文档转换PDF,并把PDF转图片,首先需要安装WPS,然后利用pypiwin32把文档转化成PDF,再利用fitz、PyMuPD把PDF转化成图片
Python调用WPS把文档转换PDF,并把PDF转图片,首先需要安装WPS,然后利用pypiwin32把文档转化成PDF,再利用fitz、PyMuPD把PDF转化成图片 快速生成表格
快速生成表格 在使用Git的过程中,不想每次都输入用户名和密码去拉取代码,所以就需要保存这些信息,那么既然有保存了,就必须有清除功能。
在使用Git的过程中,不想每次都输入用户名和密码去拉取代码,所以就需要保存这些信息,那么既然有保存了,就必须有清除功能。 Docker编译镜像出现:fetch http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.12/main/x86_64/APKINDEX.tar.gz
ERROR: http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.12/main: temporary error (try again later)
WARNING: Ignoring APKINDEX.2c4ac24e.tar.gz: No such file or directory问题
Docker编译镜像出现:fetch http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.12/main/x86_64/APKINDEX.tar.gz
ERROR: http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.12/main: temporary error (try again later)
WARNING: Ignoring APKINDEX.2c4ac24e.tar.gz: No such file or directory问题 在Mac电脑中,如何对Git的用户名和密码进行修改呢?起初不懂Mac,所以整了很久,本文将记录如何对这个进行操作,以便后期使用。
在Mac电脑中,如何对Git的用户名和密码进行修改呢?起初不懂Mac,所以整了很久,本文将记录如何对这个进行操作,以便后期使用。